Exposure
The quantity, duration and intensity of light captured by the image sensor. Exposure is controlled by three elements: ISO, Aperture and Shutter Speed  Shutter Speed Shutter Speed
The feature that controls how long the shutter is open for and therefore how much light comes into the camera and hits the image sensor.
Noise or Digital Noise
The appearance of colour dots or specks (sometimes called grain), often pronounced in shadows and darks areas.
Overexposed
A condition in which too much light reaches the sensor, making it look too light or washed out.
Av
Aperture value, identifies Aperture Priority Mode
Aperture Priority
An exposure mode that lets you set the aperture while the camera determines the shutter speed for proper exposure. If you change the aperture, or the light level changes, the shutter speed changes automatically.
ISO
The feature that controls the sensitivity of the image sensor in your camera. Low ISO is not very sensitive and good for sunny days when you don’t need a lot of light captured. At a high ISO means your image sensor is more sensitive when you need a lot of light – this is good for shooting in low light.
Stops
Stop can refer to different settings in any of the three elements that control Exposure. Aperture, Shutter Speed, and ISO settings are all divided up into "stops", even though the numbering systems are different.
Depth of Field (DOF)
The zone of sharpness in front of, and behind, the subject on which the lens is focused. Depth-of-Field (DOF) is affected by Aperture. A low aperture value will give you a very shallow or short depth of field – so the foreground and background which bracket your area of focus will be blurred. A wider or longer DOF can be achieved by a higher Aperture setting. This will bring more of the area bracketing your subject into focus.
Shutter Priority
An exposure mode that lets you select the desired shutter speed while the camera determines the aperture for proper exposure.
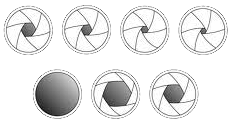  Aperture Aperture
The feature that controls the size of the lens opening when a picture is taken. If you need a lot of light you want to have a big opening (a low aperture). Measured in F-stops and often referred to as such.
F-stop (see aperture)
Technically refers to the numbers that represent the size of your lens opening. A low number gives you a large lens opening. A high number gives you a smaller lens opening.
Underexposed
A condition in which not enough light reaches the image, making it look dark.
Tv
Time value, identifies Shutter Priority Mode
Saturation
The percentage of hue in a colour. Saturated colours are called vivid, strong, or deep. Desaturated colours are called dull, weak, or washed out.
|




